Sign up for our newsletter and get 10% off!
Understanding the Causes, Symptoms, Treatments, and Prevention of Tendinopathy

Dr. Stéphane De Jésus
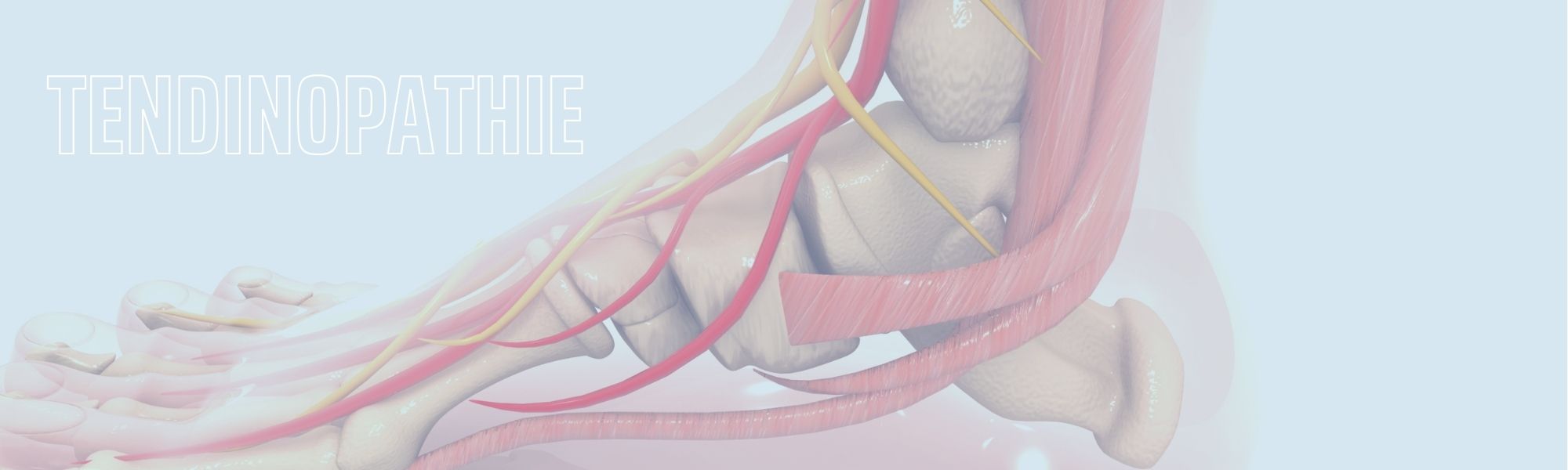
Due to its fibrillar structure, a tendon is both resistant to tension and elastic. Moreover, well-conducted athletic training can increase its strength and elasticity.
Conversely, an unusual, repeated effort on an undertrained and poorly warmed-up tendon weakens its structure, particularly at the tendon’s extremities and in the area where the greatest tensions are exerted. Sedentary lifestyles and age tend to weaken tendons, as does anormal biomechanics.
Tendinopathy, a common and often painful condition, manifests in a large number of people, from elite athletes to less active individuals. In this article, we will explore in detail what tendinopathy is, what causes it, its symptoms, how it is diagnosed, and the various treatment options available. We will also discuss preventive measures you can take to reduce your risk of developing tendinopathy.
What is Tendinopathy?
Tendinopathy is a general term used to describe any condition affecting a tendon. Tendons are fibrous connective tissues that connect muscles to bones, thereby enabling joint movement. When a tendon is subjected to excessive or abnormal stress, it can become damaged or even rupture.
Causes of Tendinopathy
Tendinopathy can be triggered by a variety of factors, including:
- Overuse: Constant repetition of a movement or activity can exert excessive strain or stress on a tendon, leading to inflammation and degeneration.
- Trauma: Sudden injuries, such as falls or sports accidents, can damage tendons and cause tendinopathy.
- Risk Factors: Age, being overweight, smoking, lack of hydration, lack of gradual progression in training, poor posture, and muscle imbalances can increase the risk of developing tendinopathy.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as arthritis, diabetes, and metabolic disorders can also contribute to the development of tendinopathy.
Symptoms of Tendinopathy
Common symptoms of tendinopathy include:
- Persistent pain around the affected tendon, which may be aggravated by physical activity.
- Painful reduction in mobility and strength in the affected area.
- The tendon may become thickened (e.g., Achilles, Patellar).
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional if you experience these symptoms, as early diagnosis can lead to a better prognosis and more effective treatment options.
Diagnosis of Tendinopathy
The diagnosis of tendinopathy generally begins with a physical examination by a doctor or physiotherapist. Imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of tendon damage
Treatments for Tendinopathy
Treatment options for tendinopathy may include:
- Rest and modification/adaptation of activities to allow the tendon to heal.
- Physiotherapy to strengthen the surrounding muscles and improve mobility.
- Posture and movement correction.
- Alternative therapies such as shockwave therapy, acupuncture, injections, PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma), peri-tendinous hyaluronic acid, and intra-tendinous collagen.
- Surgery in severe cases that are resistant to conservative treatment.
- At Ledvard, we offer Synergy6 treatment, which has proven effective for many people in relieving tendinopathy and preventing its onset. Our formulation contains molecules found in the extracellular matrix of joint elements, including bones, cartilage, synovial fluid, ligaments, and tendons.
Prevention of Tendinopathy
To reduce your risk of developing tendinopathy, you can take the following preventive measures:
- Perform adequate warm-ups before exercise to prepare the muscles and tendons for physical activity.
- Incorporate strengthening and mobility exercises into your training routine to maintain tendon strength and flexibility.
- Maintain a healthy weight and a balanced diet.
- A 12-week course of Synergy6 can also help prevent the risk of injuries.
Tendinopathy is a common condition that can affect quality of life and daily functionality. By understanding its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures, you can take steps to protect the health of your tendons and maintain an active and pain-free life. If you experience symptoms of tendinopathy, do not hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for an appropriate diagnosis and treatment.


