Sign up for our newsletter and get 10% off!
Chondroitin

Gautier Lalevée
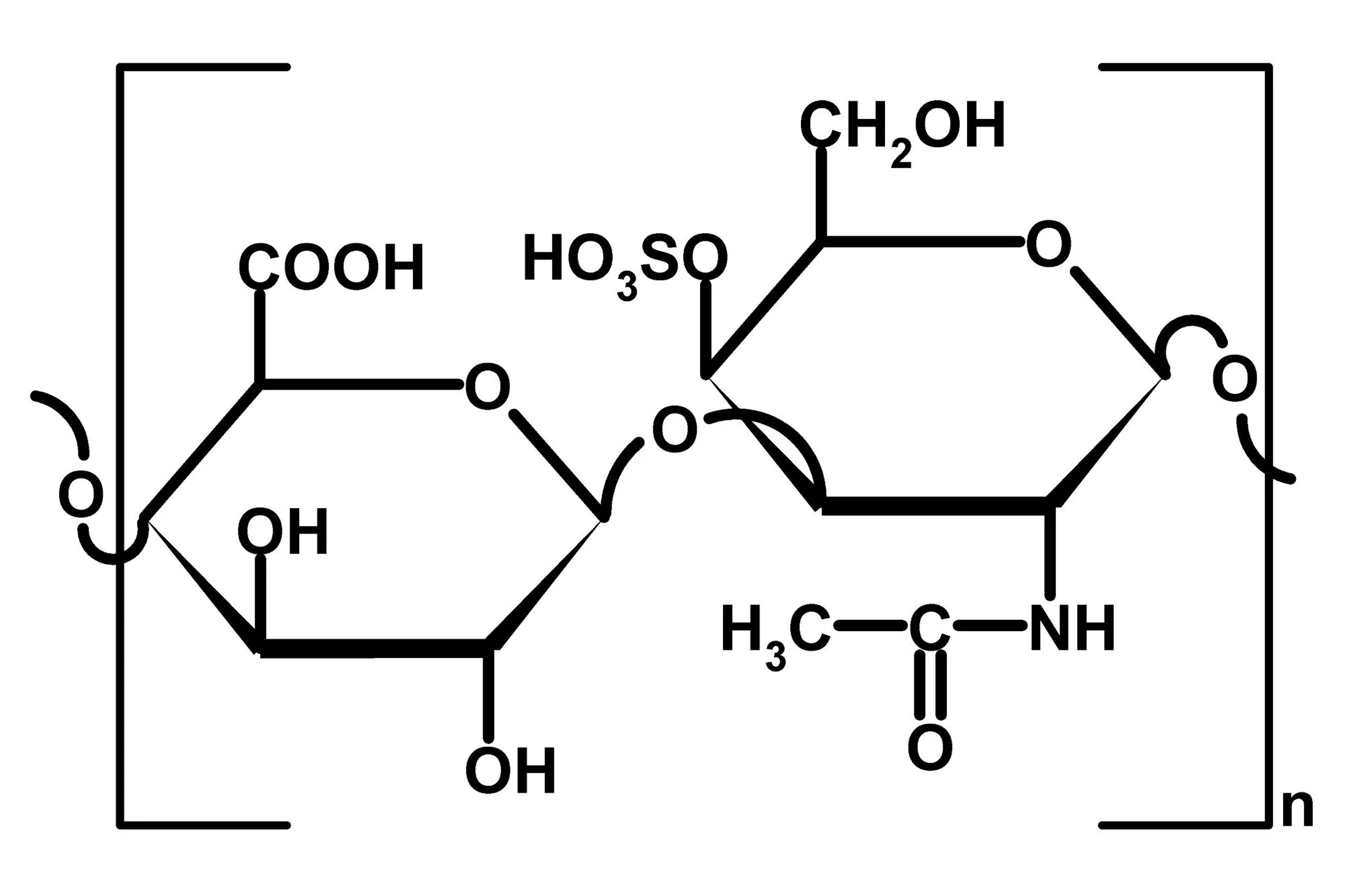
Chondroitin is a major component of cartilage and bone which, combined with glucosamine sulfate, creates a notable synergistic effect, protecting cartilage and limiting the production of free radicals.
What is chondroitin?

Chondroitin is a natural substance found in cartilage, the connective tissue that covers the ends of bones in joints. It is one of the proteoglycans, the molecules that give cartilage its strength and elasticity.
What's its role?
Chondroitin is thought to act by reducing inflammation in the joints, promoting the production of new cartilage components and inhibiting cartilage-degrading enzymes. It can also help improve joint lubrication.
Chondroitin is often combined with glucosamine in dietary supplements for the treatment of osteoarthritis. These two substances are considered “chondroprotectors”, i.e. they protect the chondrocytes, the cells present in cartilage. Ultimately, this process helps to limit degradation and strengthen the remaining structure of damaged cartilage.1
Where can it be extracted from?
Chondroitin is a naturally occurring substance in animal tissues, mainly in the cartilage of marine animals such as sharks, rays and fish. Chondroitin is generally extracted from these animal sources.
Chondroitin supplementation
Chondroitin sulfate, on the other hand, is chondroitin combined with a sulfate ion. This form of chondroitin is considered the most commonly used in dietary supplements and products for the treatment of osteoarthritis. This form improves the stability and bioavailability of chondroitin when used as a dietary supplement.
- Uebelhart, D. et al. Intermittent treatment of knee osteoarthritis with oral chondroitin sulfate: a one-year, randomized,double-blind, multicenter study versus placebo1. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 12,269-276 (2004).


